Database phần 3 - Các dữ liệu quan hệ
Quan hệ Nhiều - Một
Giả sử ta có lớp Book và lớp Author và ta có mối quan hệ Nhiều book thuộc về Một Author, khi đó ta thiết lập mối quan hệ @ManyToOne từ lớp Book tới lớp Author.
Lớp Book
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Data
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
@ManyToOne
private Author author;
private int year;
}
Lớp Author
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
@Data
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String website;
private String favoriteQuote;
}
Thử nghiệm
System.out.println("Hello World");
Author author = new Author();
author.setEmail("hoa@gmail.com");
author.setName("Hoa");
author = authorRepository.save(author);
Book book = new Book();
book.setAuthor(author);
book.setName("Harry");
book.setYear(1990);
int savedId = bookRepository.save(book).getId();
Book savedBook = bookRepository.findById(savedId).get();
System.out.println(savedBook);
Kết quả:
- Spring sẽ tự động tạo cột
author_idtừ bảngbookvà mỗi khi lưu trường author, Spring sẽ gán giá trị tương ứng
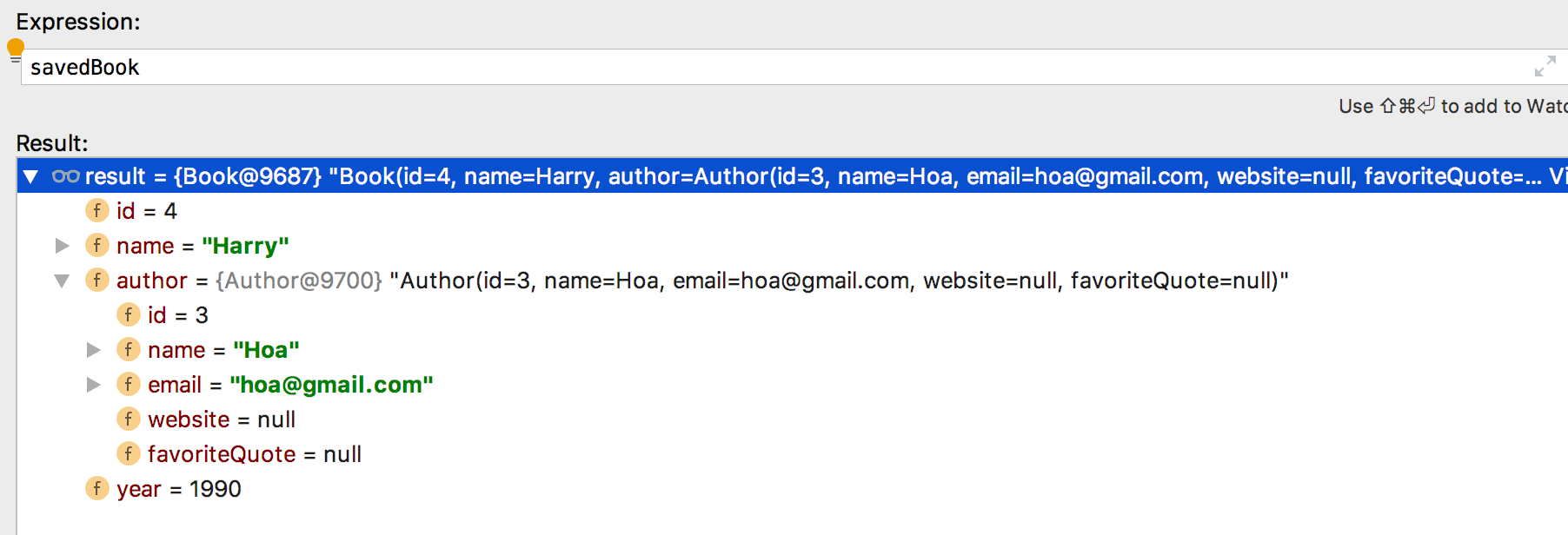
- Khi lấy lên giá trị book, spring sẽ tự động gán giá trị author tương ứng.
Quan hệ Nhiều - Nhiều
Giả sử rằng một Book sẽ có nhiều Category và ngược lại, một Category có thể có nhiều Book. Khi đó, ta xây dựng mối quan hệ @ManyToMany giữa hai lớp như sau:
Class Book
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Set;
@Data
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
@ManyToOne
private Author author;
@ManyToMany
private Set<Category> categories;
private int year;
}
Class Category
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Data
@Entity
public class Category {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String label;
}
Test
import com.voquanghoa.bookstore.models.Book;
import com.voquanghoa.bookstore.models.Category;
import com.voquanghoa.bookstore.repositories.AuthorRepository;
import com.voquanghoa.bookstore.repositories.BookRepository;
import com.voquanghoa.bookstore.repositories.CategoryRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.util.HashSet;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BookstoreApplication {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Autowired
private AuthorRepository authorRepository;
@Autowired
private CategoryRepository categoryRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BookstoreApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) {
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
Book book1 = new Book();
book1.setName("Hidden sea");
book1.setYear(1990);
Book book2 = new Book();
book2.setName("English on hand");
book2.setYear(2000);
Category category1 = new Category();
category1.setLabel("English");
category1 = categoryRepository.save(category1);
Category category2 = new Category();
category2.setLabel("Novel");
category2 = categoryRepository.save(category2);
book1.setCategories(new HashSet<>());
book1.getCategories().add(category1);
book1.getCategories().add(category2);
book2.setCategories(new HashSet<>());
book2.getCategories().add(category1);
book1 = bookRepository.save(book1);
book2 = bookRepository.save(book2);
}
};
}
}
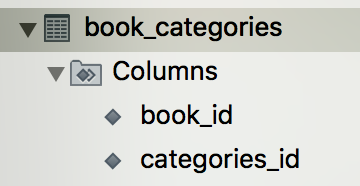
Kết quả
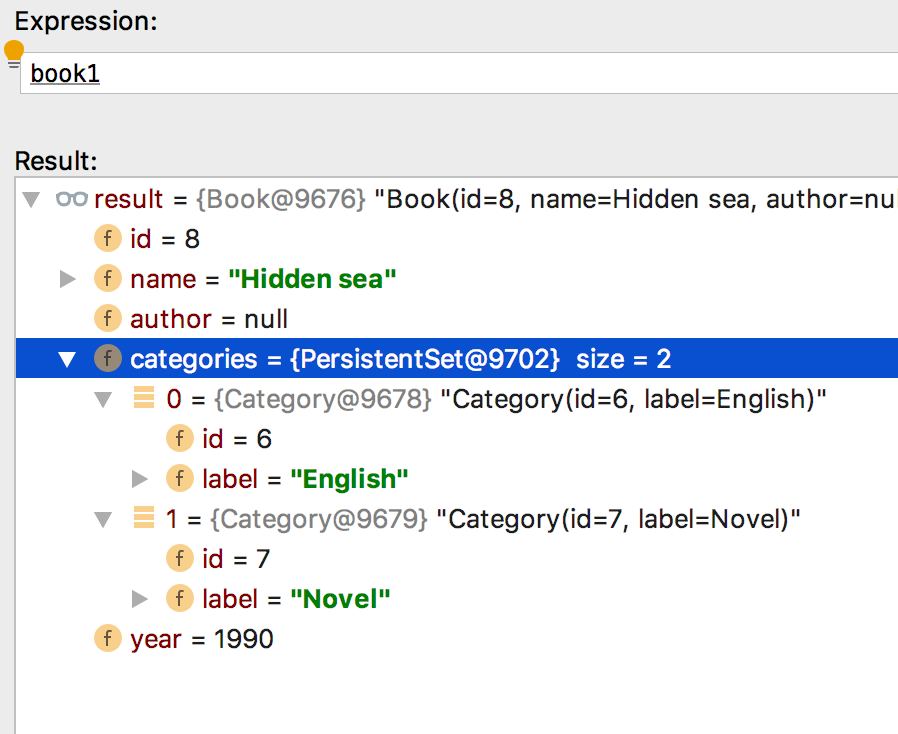
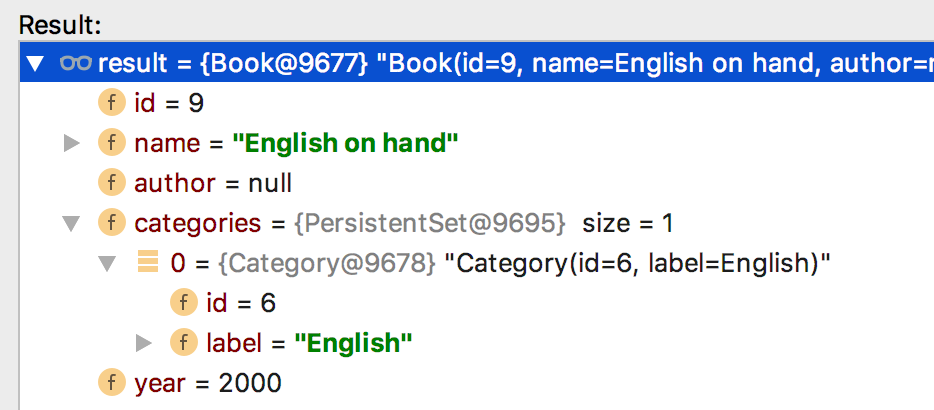
Để làm điều đó, Spring tạo ra bảng trung gian để lưu liên kết
Quan hệ Một-Nhiều
Tương tự quan hệ Nhiều-Một ở trên, ta có thể sử dụng quan hệ Một-Nhiều @OneToMany để mô tả một quan hệ giữa một Author tới nhiều Book
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
@Data
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String website;
private String favoriteQuote;
@OneToMany
private Set<Book> books;
}
Kết luận
- Bằng cách sử dụng các annontation như @ManyToOne, ta mô tả quan hệ giữa các entities
- Khi ta lưu một giá entity, spring sẽ tự động gán giá trị khóa chính cho các khóa ngoại
- Khi query một entity, spring có thể lấy entity có quan hệ đã lưu trước đó
Xem